For non-breastfed infants, strategies are developed to maximize iron absorption and reduce its deleterious impact on the gut microbiota. In this approach, the introduction of prebiotics (scGOS/lcFOS*) in infant formulas is particularly well-suited.
Prebiotics
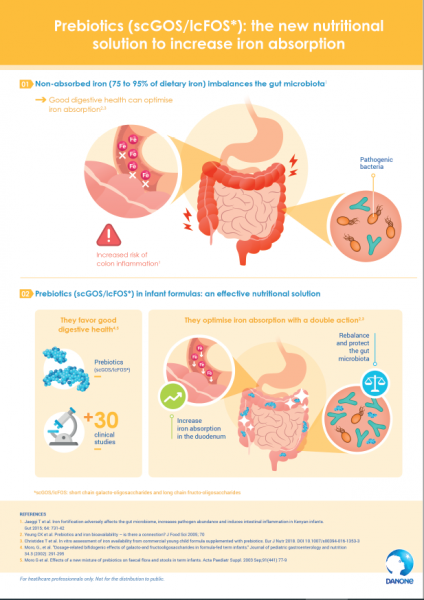
Prebiotics are undigested substrates selectively used by host bacteria, which confer a health benefit1. The most common are inulin, fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS), and galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS). Oligosaccharides prebiotics are essential components of breast milk2. They stimulate the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli) in the gut, they increase iron absorption and they oppose the deleterious effects of unabsorbed iron in the gut microbiota3-5.
The role of prebiotics in iron absorption
The prebiotics scGOS/lcFOS*, by a potential double action, promote iron absorption and rebalance the gut microbiota3,4:
Directly, in the duodenum and/or colon:
- Stimulation of the expression of iron transporters in the duodenum and/or the colon
Indirectly, by rebalancing the gut microbiota:
- pH reduction,
- Reduction from ferric to ferrous iron (a form with better bioavailability)
- Reduction of inflammation that reduces hepcidin production, which itself inhibits iron absorption
To find the potential mechanisms of prebiotics that allow the increase of iron absorption on video, click here.
Thus, prebiotic-enriched infant formulas represent an effective nutritional strategy to prevent iron deficiency in non-breastfed children by stimulating the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria, and reducing the harmful effects of unabsorbed iron3,4. This also promotes an intestinal microbiotic profile close to that of breastfed infants and optimizes their digestive health5. Moreover, the addition of prebiotics (scGOS/lcFOS*) to vitamin C reveals a synergistic effect on iron absorption4.
Find the interview with Professor Michael Zimmermann at the 11th edition of the African Meeting of Infant Nutrition (RANI) on iron absorption and infant gut health:
Infography : Prebiotics (scGOS/lcFOS*), the new nutritional solution to increase iron absorption
References
*scGOS/lcFOS: short-chain galacto-oligosaccharides and long-chain fructo-oligosaccharides.
- Gibson, et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nature rev Gastroenterol hepatol 14.8 (2017): 491-502.
- Agostoni C et al. Breast-feeding: A Commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009; 49: 112-25.
- Yeung CK et al. Prebiotics and iron bioavailability – is there a connection? J Food Sci 2005; 70: 88-92.
- Christides T et al. In vitro assessment of iron availability from commercial young child formula supplemented with prebiotics. Eur J Nutr 2016. DOI 10.1007/s00394-016-1353-3.
- Moro G et al. Dosage related bifidogenic effects of galacto– and fructo-oligosaccharides in formula-fed term infants.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002;34: 291–5.
BA20-464
